It promotes:
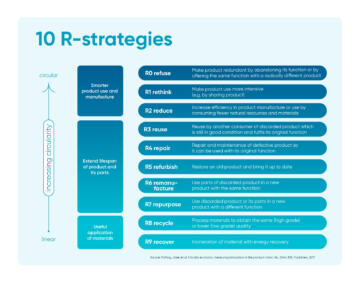
- adaptive product design that facilitates repairRepair is making a faulty product work again, allowing its use to be extended without the user parting with it, or with a view to reuseReuse designates all operations by which substances, materials or products that are not waste are used again in an identical way to their originally intended purpose. (donation, second-hand sale). and the total or partial reuse of end-of-life components (ecodesignEcodesign allows a product design to be adapted in view of its repair or a full or partial repurposing of its components at the end of its useful life.);
- manufacturing of new products using downgraded parts, components or products;
- maintenance, repair, and reuse of products;
- efficient use of resources during the various production and consumption stages;
- recyclingAny recovery operation through which waste, including organic waste, is reprocessed to become substances, materials or products that can be used for their initial function or other functions. of industrial, agricultural, or household resources and waste.
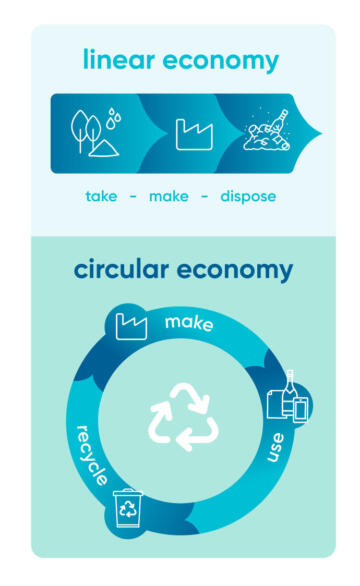
From a circular economyThe circular economy is a restorative and regenerative economy. By maintaining the value of the products, materials and resources in the economy through smart product design, repurposing and/or shared use of products, it reduces the extraction of natural resources by using resources already present in the economy. perspective, the main innovative economic models prioritise:
- using renewable, recycled or highly recyclable inputs in production processes;
- developing a sharing economy to maximise the use of unused assets within a community , providing customers with affordable and convenient access to products and services;
- shifting towards a products-as-a-service approach: customers buy a service for a limited period of time while the supplier retains ownership of the product. This incentivizes the supplier to ensure maintenance, durability, improvement and treatment of the product at the end of its life
(functionality economyThe functionality economy aims to commercialise the usage of a product rather than the product itself.); - extending lifespan of products and designing them so that they are repairable, upgradable, reusable, easy to disassemble, reprocess and recycle (ecodesign);
- recovering resources, focusing on the final stages of the products' lifecycleA product lifecycle takes into account every activity involved in the manufacture, use, transport and disposal of the product., and more specifically the recovery of integrated materials, energy and resources from end-of-life products.
Moving from a linear to a circular economy saves money, improves resource efficiencyEfficiency is focused on the productivity of resources, i.e. in an improvement in the relationship between the natural resources used and the benefit they provide in the form of a product manufactured or a service provided., creates jobs, and reduces the environmental impact of production and consumption.
Find out more:
FPS Economy
Belgium.be
Health Belgium
ABC of the Circular Economy
The circular economy often uses specific technical concepts and terminologies. That is why we have provided a glossary of the most used terms.
Efficient innovation